- HOME
- Sustainability
- Environment
- Co-existence with the Environment Initiatives
Co-existence with the Environment Initiatives
EnvironmentAddressing Climate Change
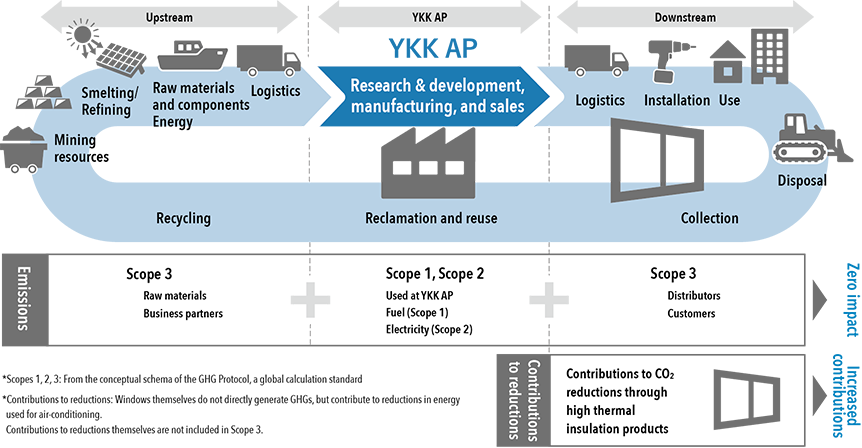
YKK AP is working to reduce CO2 emissions and address climate change in all of its business activities.
This initiative is being promoted by the Carbon Neutrality Project, led by the head of the Manufacturing Division. This project consists of seven working groups involving young engineers, and is promoting the formulation of a carbon neutrality technology roadmap and initiatives based thereon.
Aiming to achieve, relative to FY2013, a 80% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 and a 30% reduction in Scope 3 by FY2030, we will accelerate capital investment and technological development while reviewing each platform for products and monozukuri.
Furthermore, the popularization of high thermal insulation products will reduce the amount of energy used for heating and cooling, contributing not only to YKK AP’s carbon neutrality but also to that of society as a whole.
Scope 1 and 2 Initiatives
We are working to reduce the amount of fuel and electricity used in our manufacturing processes and offices. The Machinery & Engineering Department, which is responsible for developing manufacturing equipment, is improving the energy efficiency through standardization and the adoption of energy-saving technologies. In terms of fuel, we are switching from liquid fuels to natural gas. Furthermore, with a view to the future, we are developing and testing the use of hydrogen and other gases in gas burners.
We are also working on energy creation from renewable sources, such as solar, hydro, and wind. As of FY2024, we have increased the amount of renewable energy installed to nine times the FY2021 level. This accounts for approximately 7% of YKK AP’s total electricity consumption.
In order to measure our progress in reducing CO2 emissions, we are also developing a database that tracks energy consumption by facility and manufacturing site and visualizes CO2 emissions.
As of FY2024, we have reduced Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 37% relative to FY2013 levels.
Expanding the use of renewable energy
We are promoting the introduction of self-consumed renewable energy on our own premises, and have achieved a total of 16,200 kW of solar power generation at 11 locations in Japan and overseas. With the expansion of renewable energy, surplus electricity is generated, and in FY2024, we started operating a "surplus electricity sharing on-site PPA" in the Tokyo metropolitan area. We have also established a system to fully utilize 100% of the electricity generated by solar power at the Saitama Factory (new building) by supplying it to the Saitama Factory (old building) and the Saitama MADO (Window) Plant. This initiative is expected to reduce CO2 emissions by 512 tons per year. In addition, a large solar power generation facility has been installed at the Namerikawa Plant.
In March 2025, we introduced large storage batteries at our Kyushu Plant, and plan utilize surplus electricity during peak usage hours and at night. In addition, we are promoting demonstration tests of energy generation facilities tailored to regional characteristics, such as wind power and hydroelectric power generation utilizing water used in manufacturing processes. In FY2024, we achieved a reduction of 12,000 tons in CO2 emissions through the introduction of renewable energy.

Large solar power generation facility installed at the Namerikawa Plant
Scope 3 Initiatives
Scope 3 emissions account for the majority of the CO2 emissions associated with YKK AP’s business activities across entire supply chain. Of these, emissions from material procurement for products account for 80% of the total. In particular, the procurement (mining, smelting, and overseas transportation) of aluminum ingots has a significant impact, and the utilization of recycled aluminum will have the greatest impact in achieving carbon neutrality.
We have already achieved a 100% internal recycling rate, and our next challenge is to expand the utilization rate of market-obtained recycled materials (recycled raw materials such as aluminum scrap recovered from the market). Since market-obtained recycled materials contain a variety of metals, we are focusing on improving separation technologies for extracting only high-quality aluminum.
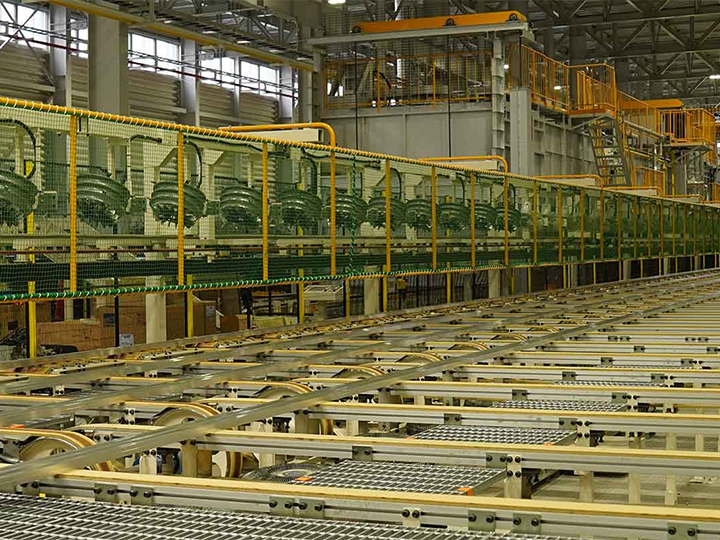
The Shikoku Plant, which introduced a dedicated aluminum recycling furnace in FY2023, reached a recycled aluminum usage rate of 80% by the end of FY2024.
We are involved, as the lead company, in the "Creation of a Toyama Resource Recycling Society Model," an industry-academia fusion hub concept project to revitalize aluminum-related industries in Toyama Prefecture, led by the University of Toyama. In this way, we are working to accelerate in-depth technical development of aluminum recycling through collaboration between industry, government, academia, and the private sector. From April 2024, a joint research course with YKK AP is being offered at Tohoku University to promote research aimed at realizing an aluminum recycling-oriented society.
We are also working to secure green aluminum raw materials by using green energy at the stage of smelting aluminum from bauxite, as well as to improve logistics efficiency by introducing double-trailer trucks and joint shipping. With respect to our business partners, we have circulated Green Procurement Guidelines and chemical substance management guidelines, and we also conduct a CSR survey based on environmental perspectives.
As of FY2024, we have reduced Scope 3 emissions by 19% relative to FY2013 levels.
Introduction of aluminum recycling furnace
YKK AP is introducing recycling furnaces in order to increase the company's ratio of input of market-obtained recycled materials to the input of aluminum raw materials. While ordinary melting furnaces can melt large quantities of market-obtained recycled materials by heating them with a burner, adding large quantities of such materials leads to oxidation and increased aluminum depletion. A dedicated recycling furnace, which uses a different method than a melting furnace, can reduce the amount of wear and tear during aluminum melting.
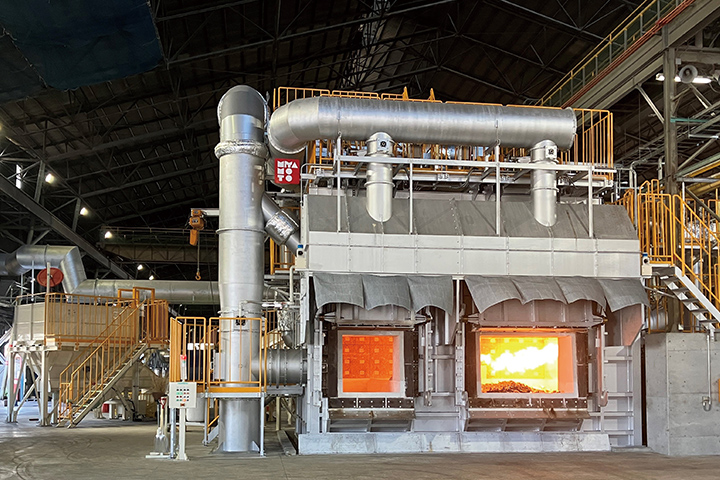
Recycling furnace at the Shikoku Plant.
At the back left is an automatic material feeder
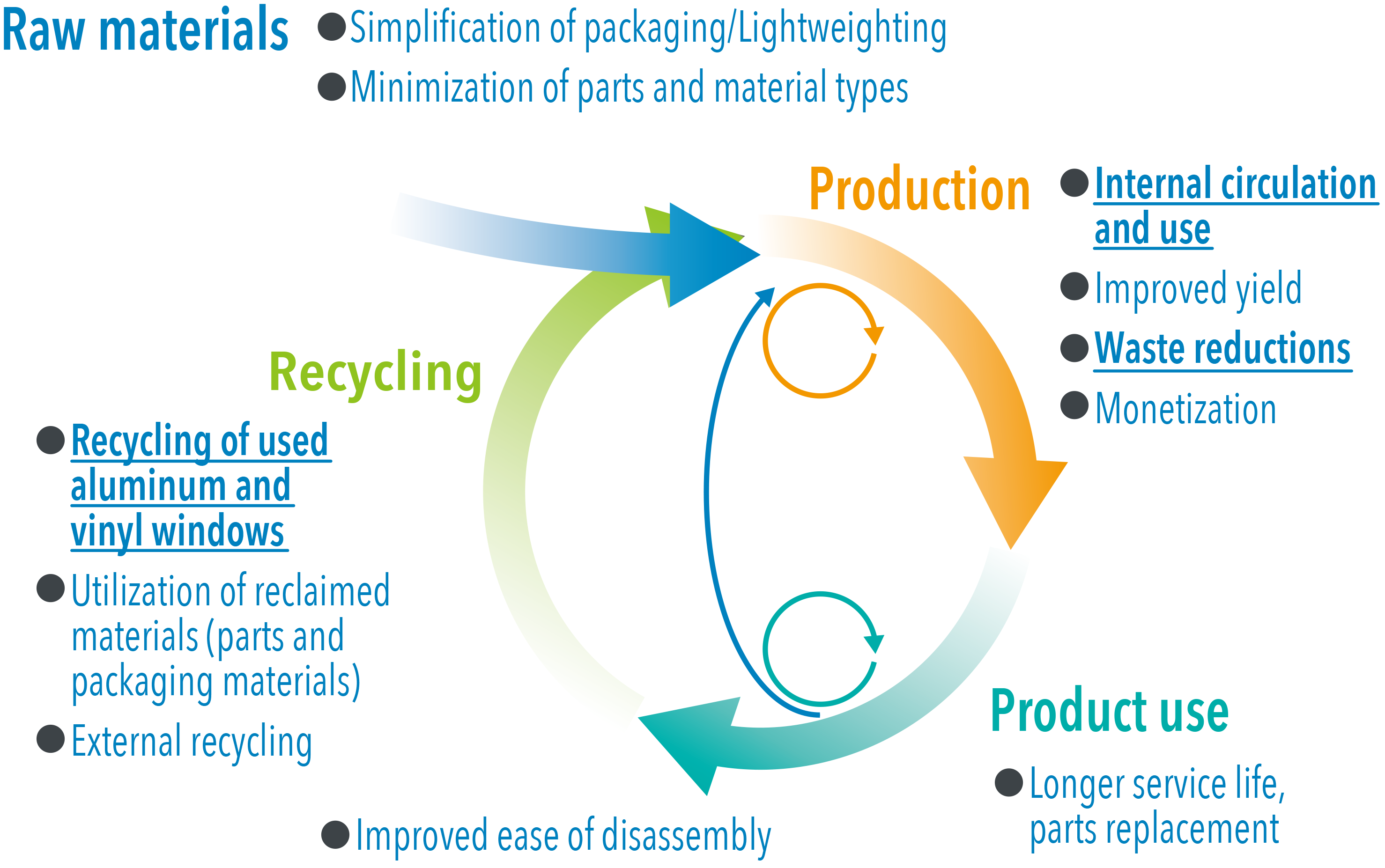
Taking on the Challenge of a Circular Economy
In pursuit of realizing a circular economy, we promote activities that are in line with the Three Rs (Reduce; Reuse; and Recycle) to reduce waste materials, and reuse and recycle materials.
To achieve "reducing input materials for products and using recycled materials," we are working to reduce input materials in packaging and product installation, and to increase the use of recycled PVC in vinyl products. This involves developing products with resource recycling in mind and establishing systems to provide products with lower environmental impact.
The recycling rate for industrial waste generated at our Japan manufacturing has already reached 100%. We are continuing our efforts to achieve a recycling rate of 99% or higher both domestically and internationally by 2030.
To "reduce industrial waste", we prioritize reducing plastic packaging materials through simplifying packaging, shifting them to returnable ones, and standardizing packing materials. Additionally, we have introduced facilities at the Kurobe Ekko Plant to produce RPF (refuse-derived paper and plastics-densified fuel) from waste plastics like film and laminate, along with recycled paper and wood chips, further promoting waste valorization.
“Reducing Input Materials and Utilizing Recycled Materials in Products” involves reducing input materials in packaging and product manufacturing, while also increasing the use of PVC recycled materials in resin products. We are working to establish mechanisms for product development that considers resource circulation and provides products with lower environmental impact.
Toward Improved Vinyl Recycling Rates
We are also actively working to improve the recycling rate for the vinyl produced during the process of manufacturing vinyl windows, as well as after use. We have installed crushing and sorting machines at each of our vinyl window manufacturing sites to reuse scrap materials as raw materials for vinyl profiles and parts for insulating glass.
Social implementation of vinyl window recycling
In order to implement recycling of vinyl windows circulating on the market, thereby reducing the amount disposed of in landfills, YKK AP is participating as a member of the "Vinyl Window Recycling Committee," which is formed mainly of industry associations. The association is engaged in industry-government-academia collaboration to establish a system to collect and recycle vinyl windows after use.
We will continue to proactively accelerate our initiatives in vinyl window recycling and aim to commercialize products based on "window-to-window" recycling, using recycled materials derived from used vinyl windows, including those from other manufacturers.

A vinyl profile made from reused vinyl scraps (gray parts are recycled materials)

Regular meeting of the Vinyl Window Recycling Committee
Implementation of Guidelines for Sustainable Design
To minimize CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain, YKK AP applies its "Sustainable Design Guidelines" during product development. We evaluate and improve products with respect to the following five items over the product lifecycle: "visualization of CO2 emissions," "standardization of packaging materials," "visualization of environmentally hazardous substances," "ease of disassembly and separation," and "Sustainable design guidelines and evaluation methods." In particular, with regard to packaging materials, we are expanding the use of reusable packaging materials and reducing the amount of plastic used.